Podiatry Services for Fort Walton Beach and Niceville FL
Many podiatric conditions can be treated in our office under the care of our Podiatrist Paul J. Kalin, DPM and our exceptional staff. In some cases, surgery will be performed at a hospital. Foot conditions involving damage to underlying tissues are best treated with surgery. Conditions involving a change in the conformation of the foot or toes are also amenable to correction with surgery. Podiatrists are specially trained in the use of a variety of surgical techniques to address these problems, to minimize pain and to prevent the loss of function of any part of the foot. Podiatrists are also familiar with all available treatment options to determine when surgery is necessary, and when it can be avoided.
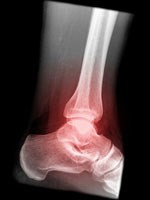
Sprains and Fractures
The foot and ankle contains a total of 26 bones. Any one of the bones can become fractured as a result of injury. Tendons are the connective tissue that connects bones to each other and holds them together. When these become strained or torn, often as a result of being hit or twisted, the result is a sprain. If a ligament is completely torn, sometime a pop is heard or felt.
Diagnosis:
Fractures can be diagnosed with the use of an X-ray, or other imaging such as a CAT scan or MRI. Sprains are often diagnosed on the basis of the type of injury and where the pain and tenderness is. Sometimes an MRI can help diagnose a specific sprain.
Treatment:
The initial treatment of either a sprain or a fracture includes rest, elevation and ice. It is important to keep weight off of the affected foot or ankle. In some cases a cast or splint is applied to minimize motion so that the foot or ankle can heal properly. In other cases surgery may be needed to repair a ligament or to stabilize a fracture.
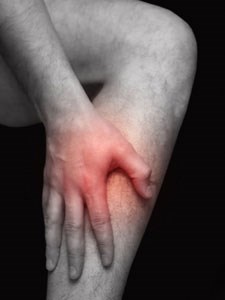
Shin Splints
Shin splints refers to pain along the shins, or the front of the leg between the knee and ankle. The pain is typically worse along the lower one-third of the leg. The muscle in this area controls upward movement of the foot, and the pain is caused by overuse and strain of this muscle. The most common cause of shin splints is athletic activity that involves running.
Diagnosis:
Shin splints are diagnosed on the basis of the typical area involved and the type of movement that increases the pain.
Treatment:
The treatment of shin splints primarily involves rest. Medications can also be used to help control pain and inflammation. Activities may need to be modified to prevent shin splints from recurring.
Without Treatment:
Shin splints may become more severe and cause pain with normal walking. Progressive damage to involved muscle can occur, especially if there is swelling. Damage to the bone to which the muscle is attached, a stress fracture, can also occur.
Service Policy
Please call (850)863-1238
